Economics Playlist
18 chapters • 0 completed
Introduction to Economics
10 topics
National Income
17 topics
Inclusive growth
15 topics
Inflation
21 topics
Money
15 topics
Banking
38 topics
Monetary Policy
15 topics
Investment Models
9 topics
Food Processing Industries
9 topics
Taxation
28 topics
Budgeting and Fiscal Policy
24 topics
Financial Market
34 topics
External Sector
37 topics
Industries
21 topics
Land Reforms in India
16 topics
Poverty, Hunger and Inequality
24 topics
Planning in India
16 topics
Unemployment
17 topics
Chapter 3: Inclusive growth
Chapter TestInclusive Growth
Inclusive growth is a pattern of economic growth that ensures fairness, equity, and opportunities for all sections of society. It reduces inequalities, promotes participation of marginalized groups, and ensures that growth is sustainable, environment-friendly, and non-discriminatory.
Inclusive growth is a pattern of economic growth that ensures fairness, equity, and opportunities for all sections of society. It reduces inequalities, promotes participation of marginalized groups, and ensures that growth is sustainable, environment-friendly, and non-discriminatory.

Inclusive vs Non-Inclusive Growth
| Aspect | Inclusive Growth | Non-Inclusive Growth |
|---|---|---|
| Distribution of Benefits | Shared fairly across all groups | Concentrated in hands of few |
| Participation | Broad participation of marginalized groups | Excludes weaker sections |
| Sustainability | Environment-friendly, gender-sensitive | Often exploitative and unsustainable |
| Regional Development | Reduces disparities among regions | Benefits limited to few regions |
Mains Key Points
Prelims Strategy Tips
Elements of Inclusive Growth
Elements of Inclusive Growth are the pillars of equitable development, ensuring that economic progress benefits all. These include agriculture development, poverty reduction, and reduction of regional disparities – supported by targeted government schemes and policies.
Elements of Inclusive Growth are the pillars of equitable development, ensuring that economic progress benefits all. These include agriculture development, poverty reduction, and reduction of regional disparities – supported by targeted government schemes and policies.
Elements of Inclusive Growth with Schemes
| Element | Focus Area | Key Schemes |
|---|---|---|
| Agriculture Development | Productivity, irrigation, market access | PM-KISAN, PMFBY, e-NAM, PM Krishi Sinchai Yojana |
| Poverty Reduction | Food security, employment, health, skill development | MGNREGA, NFSA, Ayushman Bharat, DDU-GKY |
| Regional Disparities | Balanced development, connectivity | Aspirational Districts Programme, Bharatmala, UDAN, PMGSY |
Mains Key Points
Prelims Strategy Tips
Pillars of Inclusive Growth
Inclusive growth is possible only when access to finance, skill enhancement, social development, technology, and sustainability are integrated into policy and practice.
Inclusive growth is possible only when access to finance, skill enhancement, social development, technology, and sustainability are integrated into policy and practice.
Challenges in Achieving Inclusive Growth
Despite several initiatives, India faces major challenges in achieving inclusive growth, such as inequality, jobless growth, skill gaps, digital divide, poor infrastructure, and environmental concerns. Addressing these barriers is critical for ensuring equitable and sustainable development.
Despite several initiatives, India faces major challenges in achieving inclusive growth, such as inequality, jobless growth, skill gaps, digital divide, poor infrastructure, and environmental concerns. Addressing these barriers is critical for ensuring equitable and sustainable development.
Major Challenges to Inclusive Growth
| Challenge | Impact |
|---|---|
| Rising Inequality | Wealth concentrated in hands of few, social unrest risk |
| Jobless Growth | Youth unemployment, informal sector dominance |
| Skill Gaps | Mismatch between education and industry needs |
| Digital Divide | Excludes rural poor from opportunities |
| Regional Disparities | Uneven growth, migration pressures |
| Weak Infrastructure | Hinders balanced growth and access to services |
| Gender Inequality | Low female participation, gender pay gap |
| Environmental Concerns | Climate risks, loss of livelihoods, health issues |
Mains Key Points
Prelims Strategy Tips
Way Forward for Inclusive Growth
Inclusive growth requires targeted policies in financial inclusion, skilling, social sector investment, technology use, and sustainable development. These measures ensure that economic benefits are equitably distributed and future-ready.
Inclusive growth requires targeted policies in financial inclusion, skilling, social sector investment, technology use, and sustainable development. These measures ensure that economic benefits are equitably distributed and future-ready.
Way Forward for Inclusive Growth
| Measure | Expected Impact |
|---|---|
| Financial Inclusion | Greater access to banking, credit, insurance for poor |
| Skill Development | Higher employability of youth, harnessing demographic dividend |
| Social Sector Investment | Improved health, education, sanitation, housing |
| Technological Advancement | Bridges digital divide, new opportunities for marginalized groups |
| Sustainable Growth | Green economy, reduced carbon footprint, long-term welfare |
Mains Key Points
Prelims Strategy Tips
Need for Inclusive Growth
Inclusive growth is essential for India to reduce poverty, remove inequalities, improve access to services, and ensure that economic progress benefits every section of society equally.
Inclusive growth is essential for India to reduce poverty, remove inequalities, improve access to services, and ensure that economic progress benefits every section of society equally.
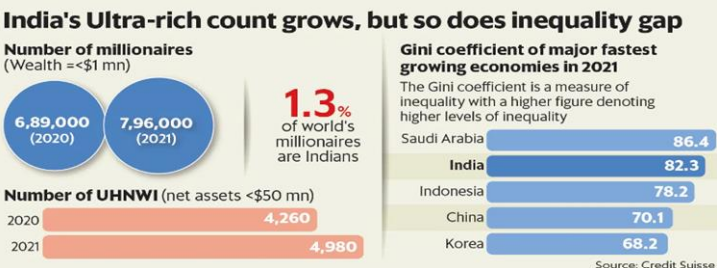
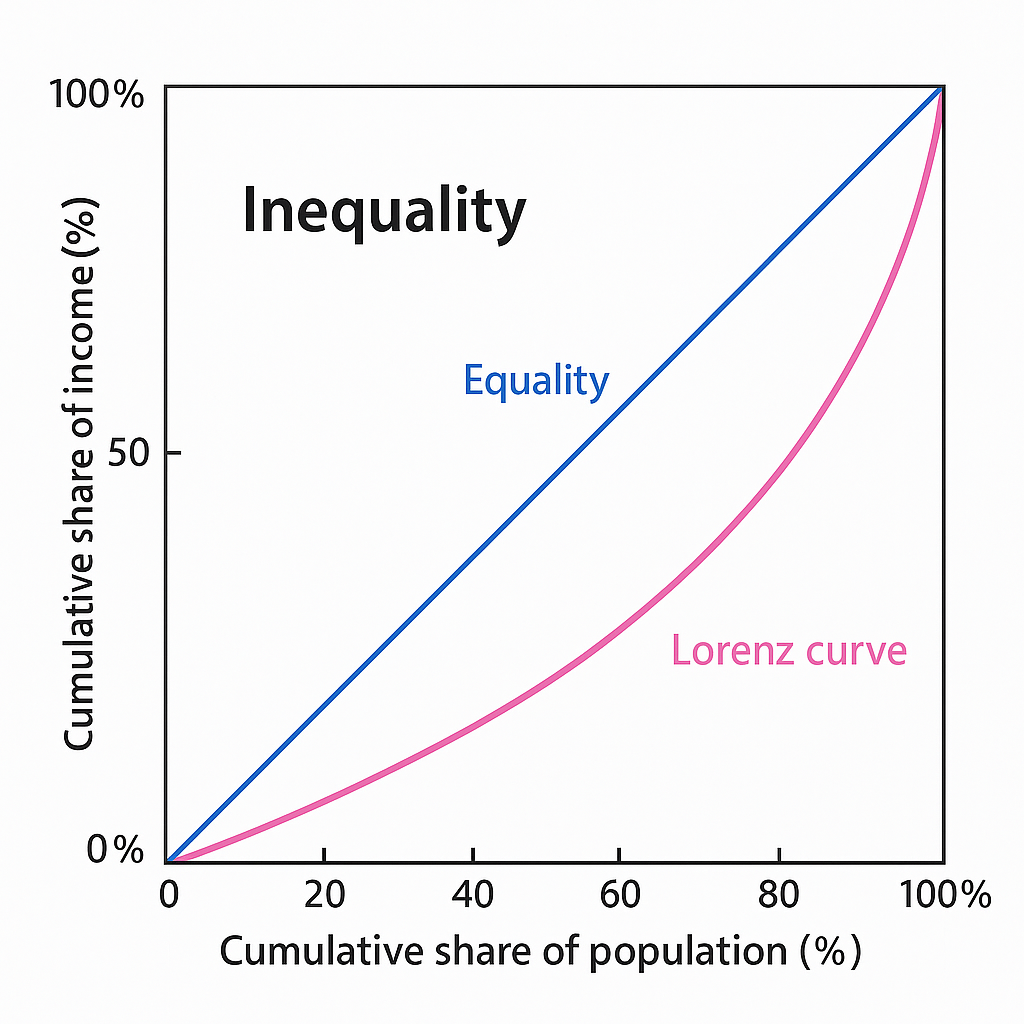
Inequality in India
Inequality refers to the unequal distribution of income, wealth, status, rights, and opportunities among individuals or groups. In India, inequality exists both in economic and social terms, affecting development and inclusivity.
Inequality refers to the unequal distribution of income, wealth, status, rights, and opportunities among individuals or groups. In India, inequality exists both in economic and social terms, affecting development and inclusivity.
Economic vs Social Inequality
| Aspect | Economic Inequality | Social Inequality |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | Unequal income and wealth distribution | Unequal access based on caste, religion, gender, etc. |
| Example | Richest 5% own 60% of wealth | Caste discrimination, gender wage gap |
| Impact | Widening rich-poor gap | Marginalisation of weaker communities |
Prelims Strategy Tips
Reasons for Inequality in India
Inequality in India arises due to a mix of historical, social, and economic factors. It is reinforced by wealth concentration, dependence on agriculture, poor social safety nets, and unequal access to opportunities.
Inequality in India arises due to a mix of historical, social, and economic factors. It is reinforced by wealth concentration, dependence on agriculture, poor social safety nets, and unequal access to opportunities.
Key Causes of Inequality in India
| Cause | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Historical Discrimination | Marginalized groups denied equal access to education, jobs, healthcare |
| Wealth Concentration | Wealth remains with a small elite, inherited by their next generations |
| Agricultural Dependence | Large workforce in low-income agriculture while GDP share shrinks |
| Tax Policy | Heavy reliance on indirect taxes burdens the poor |
| Rural-Urban Divide | Lack of infrastructure and jobs in rural areas widens income gap |
| Weak Social Policies | Absence of strong welfare schemes and inclusive policies increases inequality |
Measuring Inclusive Growth
Inclusive growth cannot be measured only by GDP. Alternative indices like Inclusive Development Index, Social Progress Index, and Financial Inclusion Index help capture broader aspects such as equity, sustainability, social welfare, and access to financial services.
Inclusive growth cannot be measured only by GDP. Alternative indices like Inclusive Development Index, Social Progress Index, and Financial Inclusion Index help capture broader aspects such as equity, sustainability, social welfare, and access to financial services.

Comparison of Inclusive Growth Indices
| Index | What it Measures | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Inclusive Development Index | Growth, inclusion, sustainability across generations | Does not cover all social dimensions |
| Social Progress Index | Outcomes of public spending on welfare | Does not capture income directly |
| Financial Inclusion Index | Access to banking, insurance, pensions, investments | Still evolving, does not reflect quality of access |
| GDP | Monetary value of goods and services | Ignores inequality, environment, welfare |
| Gini Coefficient | Income inequality | Ignores social or opportunity inequality |
Measures Taken by India for Inclusive Growth
Since Independence, India has taken multiple measures to promote inclusive growth, focusing on rapid yet equitable development. NITI Aayog’s New India @75 vision highlights inclusivity in education, health, urban development, and technology-led growth.
Since Independence, India has taken multiple measures to promote inclusive growth, focusing on rapid yet equitable development. NITI Aayog’s New India @75 vision highlights inclusivity in education, health, urban development, and technology-led growth.
Prelims Strategy Tips
Sustainable Development
Sustainable Development means meeting present needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It integrates economic growth, environmental protection, and social justice.
Sustainable Development means meeting present needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It integrates economic growth, environmental protection, and social justice.

Prelims Strategy Tips
Millennium Development Goals (MDGs)
The Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) were 8 international goals set by the United Nations in 2000, to be achieved by 2015. They focused on poverty reduction, education, health, gender equality, environment, and global cooperation.
The Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) were 8 international goals set by the United Nations in 2000, to be achieved by 2015. They focused on poverty reduction, education, health, gender equality, environment, and global cooperation.
India’s Progress on MDGs
| Goal | Target for 2015 | India’s Achievement |
|---|---|---|
| Poverty | Reduce PHCR to 23.9% | Achieved 21.9% |
| Hunger | Reduce malnutrition to 26% | Reached 40% (Not achieved) |
| Primary Education | Universal enrolment | Literacy 92-95% |
| Gender Equality | 50% women in parliament | 12.24% achieved |
| Child Mortality | 42 per 1000 | 49 per 1000 (Moderate progress) |
| Maternal Health | 109 per 100,000 | 167 per 100,000 (Not achieved) |
| Diseases | Decline in HIV, malaria, TB | On track |
| Environment | Increase green cover | Forest cover 21.23% |
| Global Partnership | Strengthened cooperation | India became donor and partner |
Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a set of 17 global goals adopted by UN member states in 2015 as part of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. They aim to end poverty, protect the planet, and ensure prosperity for all by 2030.
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a set of 17 global goals adopted by UN member states in 2015 as part of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. They aim to end poverty, protect the planet, and ensure prosperity for all by 2030.
Comparison: MDGs vs SDGs
| Aspect | MDGs (2000–2015) | SDGs (2015–2030) |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Goals | 8 Goals | 17 Goals |
| Targets | 21 Targets | 169 Targets |
| Focus | Developing countries | All countries (developed + developing) |
| Approach | Mainly social sectors (health, education) | Integrated: economic, social, environmental |
| Timeframe | 2000–2015 | 2015–2030 |
Mains Key Points
Prelims Strategy Tips
Green GDP & Energy Efficiency in India
Green GDP is an adjusted measure of GDP that accounts for environmental costs like resource depletion and pollution. India, through policies like Ujjwala, PAHAL, and Bureau of Energy Efficiency initiatives, is working towards inclusive and sustainable growth.
Green GDP is an adjusted measure of GDP that accounts for environmental costs like resource depletion and pollution. India, through policies like Ujjwala, PAHAL, and Bureau of Energy Efficiency initiatives, is working towards inclusive and sustainable growth.
Comparison: Conventional GDP vs Green GDP
| Aspect | Conventional GDP | Green GDP |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Economic output only | Economic + Environmental costs |
| Environment | Ignored | Accounted (degradation, resource use) |
| Policy Impact | Encourages growth at all costs | Encourages sustainable growth |
| Example | Building factories increases GDP | Deducts cost of deforestation in GDP |
Mains Key Points
Prelims Strategy Tips
Schemes for Inclusive Growth in India
Inclusive Growth requires policies that ensure equitable access to finance, jobs, agriculture, skills, and technology. The Government of India has launched several flagship schemes across these domains.
Inclusive Growth requires policies that ensure equitable access to finance, jobs, agriculture, skills, and technology. The Government of India has launched several flagship schemes across these domains.
Schemes for Inclusive Growth – At a Glance
| Domain | Key Schemes |
|---|---|
| Financial Inclusion | PMJDY, PMJJBY, PMSBY, APY, PMMY, JAM Trinity |
| Employment | MGNREGA, STEP-UP, SJSRY |
| Agriculture | PMKSY, e-NAM, NFSA |
| Technology | Digital India |
| Skill Development | NSDM, PMKVY, DDU-GKY, Vidya Lakshmi, SETU, AIM |
Mains Key Points
Prelims Strategy Tips
Chapter Complete!
Ready to move to the next chapter?
