Economics Playlist
18 chapters • 0 completed
Introduction to Economics
10 topics
National Income
17 topics
Inclusive growth
15 topics
Inflation
21 topics
Money
15 topics
Banking
38 topics
Monetary Policy
15 topics
Investment Models
9 topics
Food Processing Industries
9 topics
Taxation
28 topics
Budgeting and Fiscal Policy
24 topics
Financial Market
34 topics
External Sector
37 topics
Industries
21 topics
Land Reforms in India
16 topics
Poverty, Hunger and Inequality
24 topics
Planning in India
16 topics
Unemployment
17 topics
Chapter 8: Investment Models
Chapter TestInvestment and Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF)
Investment is the process of allocating funds into assets to generate returns or enhance production. It directly influences GDP through the 'I' component in the GDP formula. Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF) represents the total investment in fixed assets like machinery, buildings, and infrastructure, and is a crucial measure of economic growth and productivity.
Investment is the process of allocating funds into assets to generate returns or enhance production. It directly influences GDP through the 'I' component in the GDP formula. Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF) represents the total investment in fixed assets like machinery, buildings, and infrastructure, and is a crucial measure of economic growth and productivity.
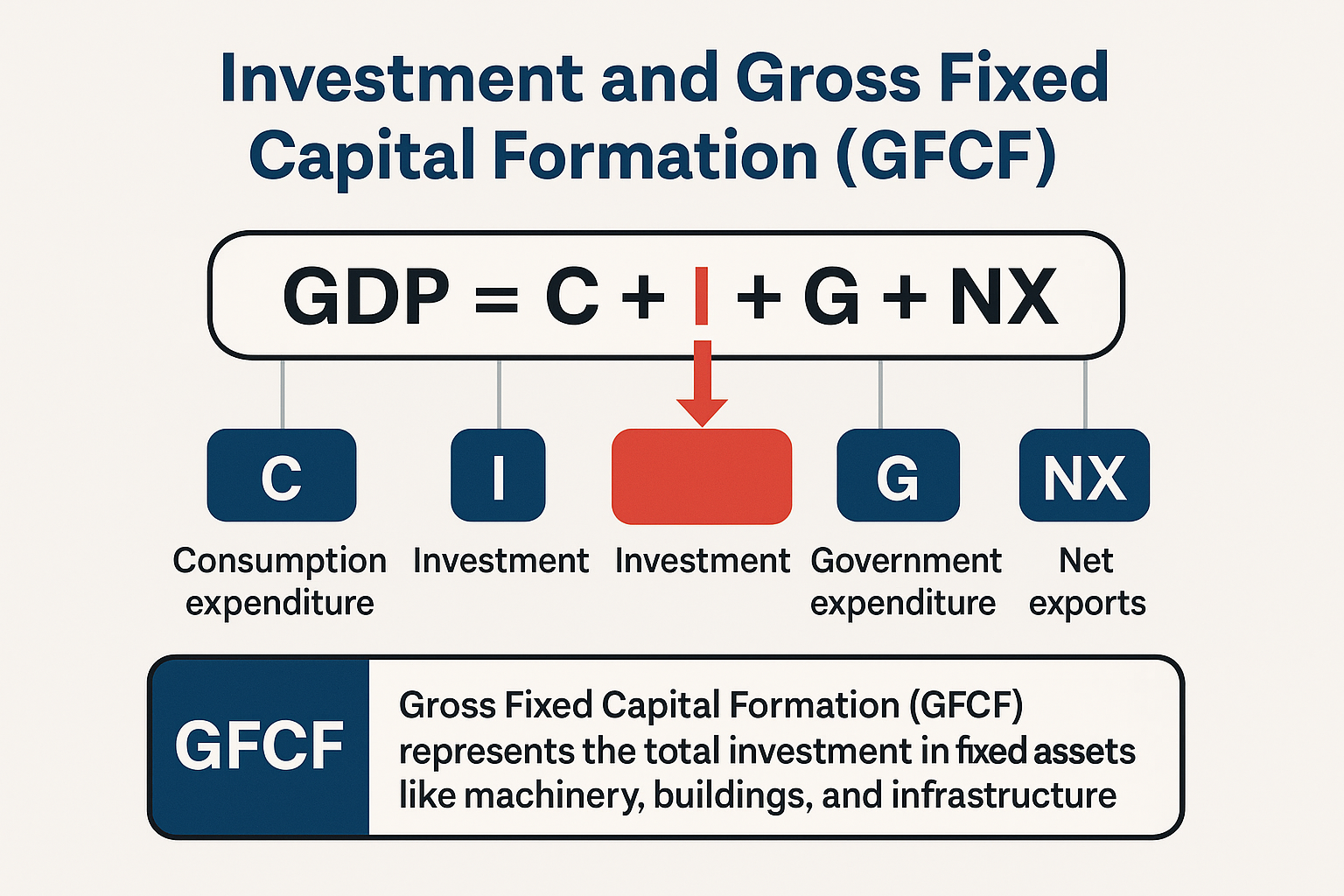
GDP Components
| Component | Meaning |
|---|---|
| C | Consumption expenditure by households |
| I | Investment in fixed assets and capital goods |
| G | Government expenditure |
| NX | Net exports (Exports Imports) |
Trends of GFCF in India
| Year | GFCF (₹ lakh crore) |
|---|---|
| 2014-15 | 32.78 |
| 2022-23 | 54.35 |
Mains Key Points
Prelims Strategy Tips
Infrastructure Investment Models – Public Investment Model
Public Investment Model refers to government-led investments in essential sectors like infrastructure, healthcare, and education. These are funded through taxes or public debt and focus on long-term development, job creation, and public welfare.
Public Investment Model refers to government-led investments in essential sectors like infrastructure, healthcare, and education. These are funded through taxes or public debt and focus on long-term development, job creation, and public welfare.
Examples of Public Investment Sectors
| Sector | Example | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure | Highways, ports, airports | Improves connectivity, trade and jobs |
| Education | Schools, scholarships, training | Skilled workforce, higher productivity |
| Healthcare | Hospitals, clinics | Better health, reduced costs |
| Renewable Energy | Solar, wind, hydro | Sustainable energy, less fossil fuel use |
| Public Safety | Police, fire services | Security and emergency response |
| Research & Development | STEM research | Innovation and technology growth |
Mains Key Points
Prelims Strategy Tips
Public Investment Model – Pros, Cons and Conclusion
While the Public Investment Model has many benefits like public welfare and correcting market failures, it also faces challenges such as inefficiency, bureaucratic delays, limited funding, and political influence. Hence, success depends on efficient management and alignment with long-term development goals.
While the Public Investment Model has many benefits like public welfare and correcting market failures, it also faces challenges such as inefficiency, bureaucratic delays, limited funding, and political influence. Hence, success depends on efficient management and alignment with long-term development goals.
Pros vs Cons of Public Investment Model
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Government sets strategic priorities | Political interference leads to inconsistent policies |
| Corrects market failures | Bureaucratic delays slow down projects |
| Focus on public welfare | Lower innovation and efficiency |
| Supports sustainable development | Funding limitations during fiscal stress |
| Absorbs risks in large projects | Can suffer from mismanagement or corruption |
Mains Key Points
Prelims Strategy Tips
Private Investment Model
The Private Investment Model refers to investments made by private individuals, companies, or institutions in assets like stocks, bonds, real estate, commodities, or startups. These investments are mainly profit-driven, unlike public investments which are guided by welfare objectives. Private investment plays a vital role in job creation, innovation, and economic growth, but it also faces challenges like lack of social focus and accountability.
The Private Investment Model refers to investments made by private individuals, companies, or institutions in assets like stocks, bonds, real estate, commodities, or startups. These investments are mainly profit-driven, unlike public investments which are guided by welfare objectives. Private investment plays a vital role in job creation, innovation, and economic growth, but it also faces challenges like lack of social focus and accountability.
Examples of Private Investment
| Type | Example | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Stocks | Buying company shares | Dividends + capital gain |
| Bonds | Govt. or corporate bonds | Fixed interest income |
| Real Estate | Rental/commercial property | Rental income, asset growth |
| Commodities | Gold, silver, oil | Hedge against inflation |
| Venture Capital | Funding startups | Equity ownership, high returns |
| Private Equity | Buying/restructuring companies | Profit by performance improvement |
Pros vs Cons of Private Investment
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Encourages risk-taking & innovation | Profit motive may ignore welfare |
| Creates jobs & competitiveness | Job insecurity for workers |
| Drives green & sustainable growth | Regulatory & transparency issues |
| Major contributor to India’s growth | Neglect of low-profit rural/essential sectors |
Mains Key Points
Prelims Strategy Tips
Public-Private Partnership (PPP) Model
A Public-Private Partnership (PPP) is a cooperative arrangement between the government and private sector companies to finance, build, and manage public infrastructure and services. It combines public welfare objectives with private efficiency and investment. PPPs are important in countries like India to bridge infrastructure gaps, reduce government burden, and increase efficiency.
A Public-Private Partnership (PPP) is a cooperative arrangement between the government and private sector companies to finance, build, and manage public infrastructure and services. It combines public welfare objectives with private efficiency and investment. PPPs are important in countries like India to bridge infrastructure gaps, reduce government burden, and increase efficiency.
PPP in India – Key Aspects
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Partnership between government & private sector to build/manage projects |
| Aim | Bridge infrastructure gap, improve efficiency, attract investment |
| Examples | Highways (NHAI BOT projects), Airports (Delhi, Mumbai), Metro rail |
| Government Support | VGF, IIPDF, IIFCL loans, FDI allowance |
Mains Key Points
Prelims Strategy Tips
Models of Public-Private Partnership (PPP)
PPP models are different frameworks that define how responsibilities, risks, and ownership are shared between government and private players while developing infrastructure or services. Each model specifies who pays, who builds, who operates, and who ultimately owns the project.
PPP models are different frameworks that define how responsibilities, risks, and ownership are shared between government and private players while developing infrastructure or services. Each model specifies who pays, who builds, who operates, and who ultimately owns the project.
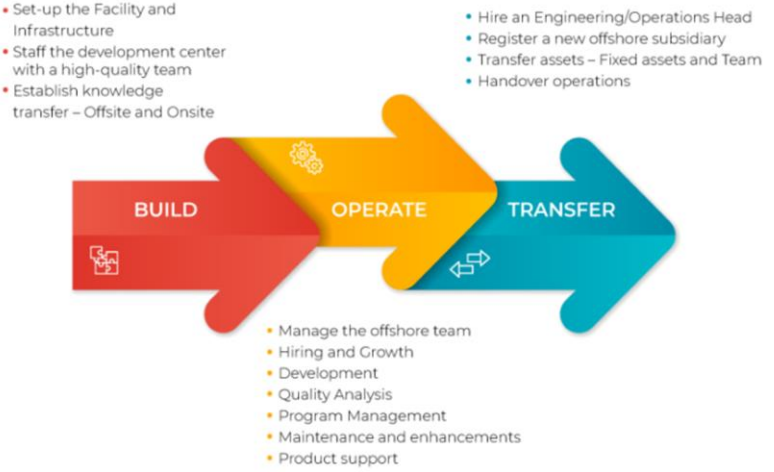
PPP Models – Who Does What?
| Model | Who Pays? | Who Builds? | Who Owns? | Who Operates? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPC | Government | Private (Engineering only) | Government | Government |
| BOT | Private | Private | Govt after concession | Private till concession |
| HAM | Govt (40%) + Private (60%) | Private | Govt after completion | Private till payment period |
| BOO | Private | Private | Private (till period) | Private |
| BOOT | Private | Private | Govt after concession | Private till concession |
| DBFO | Private | Private | Govt after concession | Private |
| BLOT | Private | Private | Govt after lease ends | Private (lease period) |
| LDO | Private | Private (development) | Government | Private (lease period) |
Mains Key Points
Prelims Strategy Tips
Vijay Kelkar Committee Suggestions on PPPs
The Vijay Kelkar Committee (2015) was set up to review and improve PPP (Public-Private Partnership) frameworks in India. It focused on shifting from fiscal benefits to service delivery, risk allocation, and institutional reforms for effective PPP implementation.
The Vijay Kelkar Committee (2015) was set up to review and improve PPP (Public-Private Partnership) frameworks in India. It focused on shifting from fiscal benefits to service delivery, risk allocation, and institutional reforms for effective PPP implementation.
Other Types of Investment Models
| Category | Sub-Type | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Based on Source | Domestic Investment Model | Funds come from within India – includes public, private, or PPP investments. |
| Based on Source | Foreign Investment Model | Funds come from outside India – can be 100% FDI or a mix of domestic + foreign. |
| Based on Destination | Sector-Specific Investment Model | Investments target specific zones/sectors like SEZs or Multi-Product Industrial Zones. |
| Based on Destination | Cluster Investment Model | Investments focus on industry clusters, e.g., food processing or textile hubs. |
Mains Key Points
Prelims Strategy Tips
Development Models Used in the Planning Process
Three important models – Harrod-Domar, Solow-Swan, and Feldman-Mahalanobis – provide different perspectives on how savings, investment, capital, technology, and government intervention affect long-term economic growth.
Three important models – Harrod-Domar, Solow-Swan, and Feldman-Mahalanobis – provide different perspectives on how savings, investment, capital, technology, and government intervention affect long-term economic growth.
Comparison of Development Models
| Model | Key Focus | Strength | Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Harrod-Domar | Savings & Investment | Simple link between savings and growth | Ignores demand issues & real-world complexity |
| Solow-Swan | Capital & Technology | Explains long-term growth & steady state | Assumes smooth tech progress |
| Feldman-Mahalanobis | Govt. Intervention in Capital Goods & Heavy Industry | Shaped India's planning; Focus on infrastructure | Risk of inefficiency & corruption |
Mains Key Points
Prelims Strategy Tips
Rao–Manmohan Model & Miscellaneous Investment Terms
The Rao–Manmohan Model (1991 reforms) was a turning point in Indian economy. Before 1991, India’s economy was closed and controlled by the government. After this model, India opened its doors to the world by reducing restrictions, allowing foreign companies to invest, and encouraging private businesses. This is also called LPG reforms (Liberalisation, Privatisation, Globalisation). Along with this, India also uses special investment methods like Swiss Challenge, Turnkey Projects, and Viability Gap Funding to support infrastructure and PPP projects.
The Rao–Manmohan Model (1991 reforms) was a turning point in Indian economy. Before 1991, India’s economy was closed and controlled by the government. After this model, India opened its doors to the world by reducing restrictions, allowing foreign companies to invest, and encouraging private businesses. This is also called LPG reforms (Liberalisation, Privatisation, Globalisation). Along with this, India also uses special investment methods like Swiss Challenge, Turnkey Projects, and Viability Gap Funding to support infrastructure and PPP projects.
Key Mechanisms Supporting Investments
| Mechanism | Purpose (Simple Explanation) |
|---|---|
| Swiss Challenge | Private proposal → govt invites bids → original proposer can match best bid |
| Turnkey Project | Contractor designs + builds → govt gets ready project at fixed cost |
| VGF | Govt. pays up to 40% support for socially important projects |
| IIPDF | Money for project studies before launch |
| IIFCL | Loans for long-term infrastructure projects |
Mains Key Points
Prelims Strategy Tips
Chapter Complete!
Ready to move to the next chapter?
