Economics Playlist
18 chapters • 0 completed
Introduction to Economics
10 topics
National Income
17 topics
Inclusive growth
15 topics
Inflation
21 topics
Money
15 topics
Banking
38 topics
Monetary Policy
15 topics
Investment Models
9 topics
Food Processing Industries
9 topics
Taxation
28 topics
Budgeting and Fiscal Policy
24 topics
Financial Market
34 topics
External Sector
37 topics
Industries
21 topics
Land Reforms in India
16 topics
Poverty, Hunger and Inequality
24 topics
Planning in India
16 topics
Unemployment
17 topics
Chapter 9: Food Processing Industries
Chapter TestFood Processing Industries
The Food Processing Industry converts raw farm products (like grains, fruits, vegetables, milk, meat) into consumable, packaged or ready-to-eat food using physical, chemical, and mechanical methods. It connects agriculture with industry, creates jobs, reduces food wastage, and contributes to exports.
The Food Processing Industry converts raw farm products (like grains, fruits, vegetables, milk, meat) into consumable, packaged or ready-to-eat food using physical, chemical, and mechanical methods. It connects agriculture with industry, creates jobs, reduces food wastage, and contributes to exports.
Food Processing – Key Aspects
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Growth Rate (FY15–21) | 8.3% annually |
| Contribution to Manufacturing GVA | 10.54% (2020-21) |
| Contribution to Agriculture GVA | 11.57% (2020-21) |
| Employment (Registered Sector) | 20.32 lakh people |
| Employment (Unregistered Sector) | 51.11 lakh people |
| Share in Exports | 10.9% of India’s exports (2021-22) |
Mains Key Points
Prelims Strategy Tips
Supply Chain of Food Processing Sector
The supply chain of the food processing industry is the journey of food from farms to consumers. It includes farmers (suppliers), food processing companies (manufacturers), and distribution networks (retailers, wholesalers, exporters). Each stage adds value and ensures food reaches people safely and efficiently.
The supply chain of the food processing industry is the journey of food from farms to consumers. It includes farmers (suppliers), food processing companies (manufacturers), and distribution networks (retailers, wholesalers, exporters). Each stage adds value and ensures food reaches people safely and efficiently.
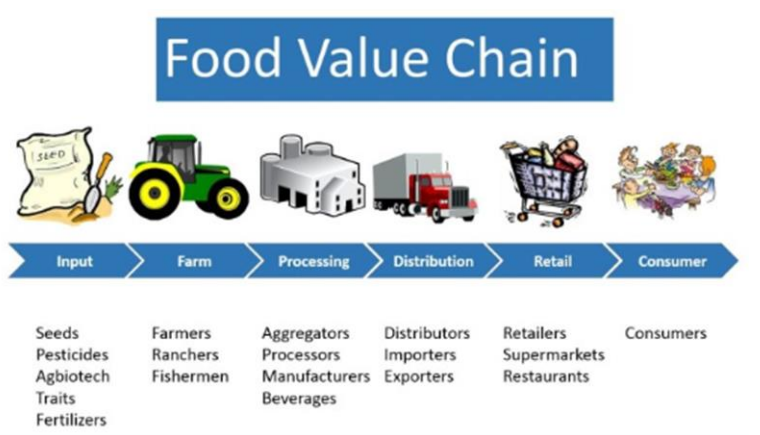
Supply Chain of Food Processing – Stages
| Stage | Role |
|---|---|
| Farmers (Suppliers) | Provide raw crops, milk, meat, fruits, vegetables. |
| Food Processing Companies | Convert raw materials into usable packaged products. |
| Distribution Network | Retailers, supermarkets, exporters deliver products to consumers. |
Importance of Food Processing Industry
| Aspect | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Food Wastage Reduction | Cuts annual losses (₹90,000 crore in India). |
| Infrastructure | Better storage, transport, processing reduces spoilage. |
| Nutrition | Fortification helps reduce malnutrition. |
| Exports | Boosts India’s share in global food trade. |
| Employment | Direct and indirect jobs for millions. |
| Crop Diversification | Encourages farmers to grow diverse crops. |
Mains Key Points
Prelims Strategy Tips
Key Factors Driving Growth of Food Processing Industry
India’s food processing industry is growing rapidly due to demographic dividend, rising incomes, government support, digital transformation, innovation, and agri-tech integration. These factors are reshaping demand, improving efficiency, and boosting exports.
India’s food processing industry is growing rapidly due to demographic dividend, rising incomes, government support, digital transformation, innovation, and agri-tech integration. These factors are reshaping demand, improving efficiency, and boosting exports.
Factors Driving Food Processing Industry
| Factor | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Demographic Dividend | Young population, urbanisation, and rising incomes increase demand for processed foods. |
| Digital Revolution | Tech platforms connect farmers with businesses, reducing middlemen and wastage. |
| Government Policies | Schemes like PLISFPI and 100% FDI boost investments and exports. |
| Innovation | New healthy and convenient products reshape consumer choices. |
| Agri-Tech | AI and digital tools improve crop quality and supply chain efficiency. |
Mains Key Points
Prelims Strategy Tips
Export Potential and Global Competitiveness of Indian Processed Foods
India exports over 10,000 products globally, with food and agricultural products contributing about 11% of total exports. India’s agri-exports were $52.5 billion in 2022-23 and are expected to reach $100 billion by 2030, with major items like rice, sugar, spices, and marine products leading the basket.
India exports over 10,000 products globally, with food and agricultural products contributing about 11% of total exports. India’s agri-exports were $52.5 billion in 2022-23 and are expected to reach $100 billion by 2030, with major items like rice, sugar, spices, and marine products leading the basket.
India’s Food Export Profile
| Category | Share/Details |
|---|---|
| Global Rank | 18th largest exporter (1.8% share in world exports) |
| Agri-export value 2022-23 | $52.5 billion |
| Target by 2030 | $100 billion |
| Top Products | Rice, sugar, spices, oil meals (51.5% share) |
| Other Exports | Coffee, tea, tobacco, fruits, vegetables, dairy, meat, seafood |
Mains Key Points
Prelims Strategy Tips
Government Policy Initiatives and Measures for Food Processing Industry
The Government of India has launched several missions, schemes, and reforms to strengthen the food processing industry. These initiatives focus on decentralisation, investment promotion (FDI), infrastructure development, safety regulations, and formalisation of micro-enterprises.
The Government of India has launched several missions, schemes, and reforms to strengthen the food processing industry. These initiatives focus on decentralisation, investment promotion (FDI), infrastructure development, safety regulations, and formalisation of micro-enterprises.
Key Government Initiatives for Food Processing
| Initiative | Year | Objective |
|---|---|---|
| National Mission on Food Processing (NMFP) | 2012 | Decentralisation of schemes; state & district role |
| FDI in Food Sector | Liberalised in 2016+ | 100% FDI via automatic route; supply chain strengthening |
| PMFME Scheme | 2020 | Formalise micro-units; ODOP approach; 2 lakh enterprises support |
Mains Key Points
Prelims Strategy Tips
Pradhan Mantri Kisan SAMPADA Yojana (PMKSY)
PMKSY (Scheme for Agro-Marine Processing and Development of Agro-Processing Clusters) was approved in 2017 to modernize infrastructure, reduce food wastage, and strengthen supply chains from farm to retail. By Dec 2022, 677 projects had been completed.
PMKSY (Scheme for Agro-Marine Processing and Development of Agro-Processing Clusters) was approved in 2017 to modernize infrastructure, reduce food wastage, and strengthen supply chains from farm to retail. By Dec 2022, 677 projects had been completed.
Schemes under PMKSY
| Scheme | Objective/Benefit |
|---|---|
| Mega Food Parks | ₹50 crore support; job creation; shared facilities |
| Cold Chain Infrastructure | Integrated cold chain from farm to consumer |
| Unit Scheme | Expansion of processing capacity; reduce wastage |
| Agro-Processing Clusters | Cluster approach near production areas |
| Backward & Forward Linkages | Stronger farm-to-market integration |
| Food Safety Infra | Quality testing & assurance |
| Human Resources & R&D | Efficient tech and packaging innovations |
Mains Key Points
Prelims Strategy Tips
Schemes Supporting Food Processing Industry
India has introduced multiple schemes like the Production Linked Incentive (PLI), Operation Greens, Gram Samriddhi Yojana, TRIFOOD Project, and the NABARD Food Processing Fund to strengthen the food processing industry, reduce wastage, increase exports, and improve farmer incomes.
India has introduced multiple schemes like the Production Linked Incentive (PLI), Operation Greens, Gram Samriddhi Yojana, TRIFOOD Project, and the NABARD Food Processing Fund to strengthen the food processing industry, reduce wastage, increase exports, and improve farmer incomes.
Key Schemes for Food Processing Industry
| Scheme | Year/Outlay | Focus Area |
|---|---|---|
| PLI for Food Processing | 2022; ₹10,900 crore + ₹800 crore (millets) | Marine, fruits, vegetables, RTE/RTC, millet-based products |
| Operation Greens | 2018-19; expanded 2021-22 | TOP crops → 22 perishables; storage & transport subsidy |
| Gram Samriddhi Yojana | 2020s; ₹3000 crore (World Bank) | Rural, unorganised food processors |
| TRIFOOD Project | Ongoing | Tribal forest gatherers; MFP processing |
| Food Processing Fund | By NABARD; ₹2000 crore corpus | Affordable loans for units in Mega Food Parks |
Mains Key Points
Prelims Strategy Tips
Draft New Food Processing Policy, Krishi UDAN 2.0 and NABARD’s Role
The Draft National Food Processing Policy (2021) aims to transform India's food processing sector with higher investments, sustainability, and competitiveness. Complementary schemes like Krishi UDAN 2.0 and NABARD’s financing initiatives further strengthen food logistics, storage, and processing infrastructure.
The Draft National Food Processing Policy (2021) aims to transform India's food processing sector with higher investments, sustainability, and competitiveness. Complementary schemes like Krishi UDAN 2.0 and NABARD’s financing initiatives further strengthen food logistics, storage, and processing infrastructure.
Key Initiatives for Food Processing Sector
| Scheme/Policy | Year | Focus Area |
|---|---|---|
| Draft Food Processing Policy | 2021 | Investment growth, sustainability, competitiveness |
| Krishi UDAN 2.0 | 2021 | Transport of perishables from remote regions |
| NABARD – Food Processing Fund | 2014-15 | Affordable loans for Designated Food Parks |
| NABARD – Warehouse Infrastructure Fund | 2010s | Scientific warehouses & APMC storage support |
Mains Key Points
Prelims Strategy Tips
Food Fortification in India
Food fortification is the deliberate addition of micronutrients (like iron, iodine, vitamins, folic acid, zinc) to commonly consumed foods to improve public health and fight malnutrition. It is a complementary measure, not a replacement for a balanced diet.
Food fortification is the deliberate addition of micronutrients (like iron, iodine, vitamins, folic acid, zinc) to commonly consumed foods to improve public health and fight malnutrition. It is a complementary measure, not a replacement for a balanced diet.
Food Fortification – Key Facts
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Adding micronutrients (iron, iodine, vitamins, zinc) to staple foods |
| Objective | Correct deficiencies, prevent malnutrition diseases like anaemia & goitre |
| NFHS-4 Data | 58.4% children & 53.1% women anaemic |
| Nature | Currently voluntary, not mandatory |
| Economic Return | ₹1 spent = ₹9 benefit (Copenhagen Consensus) |
Mains Key Points
Prelims Strategy Tips
Chapter Complete!
Ready to move to the next chapter?
